CKA [Storage] – Security Context讲解
官方文档:https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/security-context/
为什么需要Security Context?
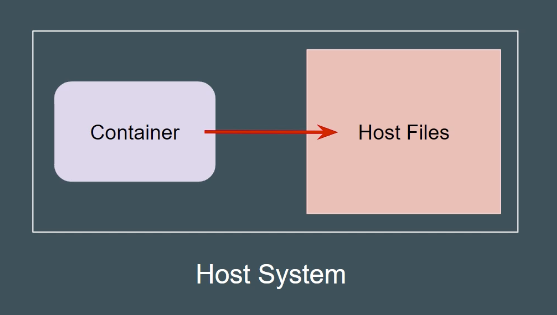
Kubernetes 默认运行container是Root权限的,如果container被攻击来了,那么攻击者就能通过container直接去到宿主机安装监听器等等。所以Security Context的作用就是为Pod 设置权限,把权限boundry在pod,而无法去更改到宿主机的东西。
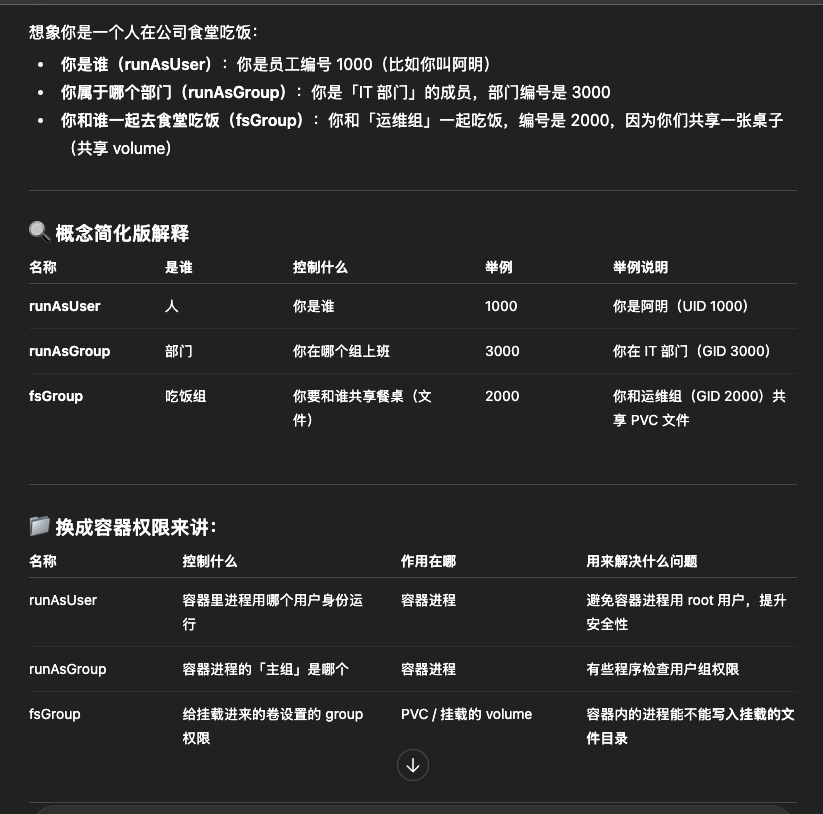
runAsUser , runAsGroup , gsGroup的区别

实践测试【HostPath Volume Mount】
1. 创建pod, 并且设置好了Security Context
kubectl apply -f pod1.yamlapiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: controlled-pod
spec:
securityContext:
runAsUser: 1000
runAsGroup: 2000
fsGroup: 3000
containers:
- name: demo-container
image: busybox:latest
command: ["sleep", "36000"]
volumeMounts:
- name: host-root
mountPath: /host
volumes:
- name: host-root
hostPath:
path: / 【进入container】
kubectl exec -it controlled-pod -- sh
【查看当下的id是否不再是root】
id
【创建文件】
touch /host/tmp/test.txt
【查看权限】
ls -l /host/tmp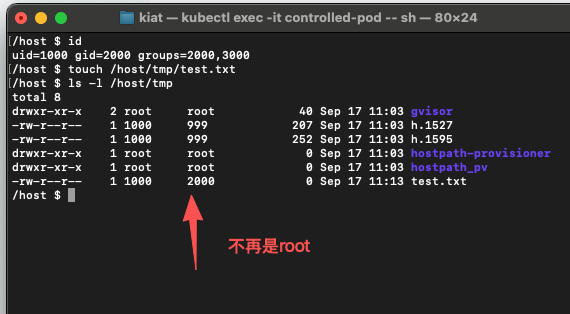
2. hostpath_pv文件的权限是root的,我们可以尝试去改看看,结果是肯定改不到的
【1. 使用vi 改root权限的文件】
- vi /host/tmp/hostpath_pv
【2. 打几个字后,进行修改】
- i
- 输入几个字,然后按esc
- :wq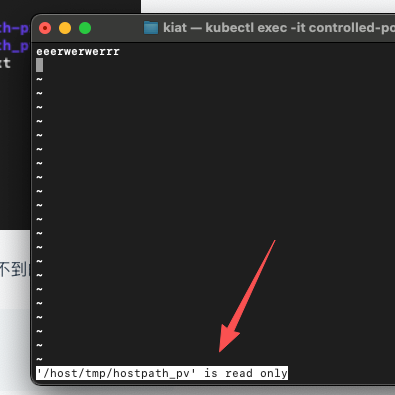
实践测试【EmptyDir Volume】
1. 创建pod
kubectl apply -f pod2.yamlapiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: fsgroup-pod
spec:
securityContext:
runAsUser: 1000
runAsGroup: 2000
fsGroup: 3000
volumes:
- name: host-root
emptyDir: {}
containers:
- name: demo-container
image: busybox:latest
command: ["sleep", "36000"]
volumeMounts:
- name: host-root
mountPath: /host2. 创建文件和查看权限
【进入container】
kubectl exec -it fsgroup-pod -- sh
【创建文件】
touch /host/test.txt
【查看权限】
ls -l /host
结论
由于实践2的所挂在的Volume是EmptyDir,所以使用的group权限就是fsGroup写的3000, 如果是hostPath本机的storage的话就是2000而已
![]()
Facebook评论